
If you are self-employed, you may need to file Schedule C to report the gross profit or loss from your business. Schedule C to Form 1040, Profit or Loss From Business (Sole Proprietorship) Additionally, you must prepare a Schedule B with the name of each payer and the amount of interest received if the total taxable interest is over that $1,500 threshold. In many cases, you’ll have to pay tax on the interest the form lists and report it on your tax return.Īll amounts listed on the form need to be added to your return. You might receive a Form 1099-INT from banks or other financial institutions if they paid you a certain amount of interest on your deposits. Once completed, these totals also transfer over to Form 1040. If you had over $1,500 in taxable interest or ordinary dividends from your bank accounts and investments, you might have to file Schedule B to report the amounts.Īdditionally, if you have any foreign bank or investment accounts or receive distributions from certain foreign trusts, you must report that information on this schedule. Once you’re finished, your total deduction amount is then added to Form 1040. If you don’t have expenses in a certain category, simply skip over it. You also don’t have to complete every line of the schedule. In some cases, you might not be able to deduct the full amounts. Strict rules apply for calculating and claiming these deductions, however. The schedule has seven categories of expenses, including charitable donations, medical expenses, and mortgage interest. And if your total deductible personal expenses are greater than the standard deduction amount set by the IRS, you can itemize them using Schedule A.
You might hear people say that some personal expenses are “deductible” from your gross income to potentially lower the amount of taxes you have to pay. Schedule A to Form 1040, Itemized Deductions
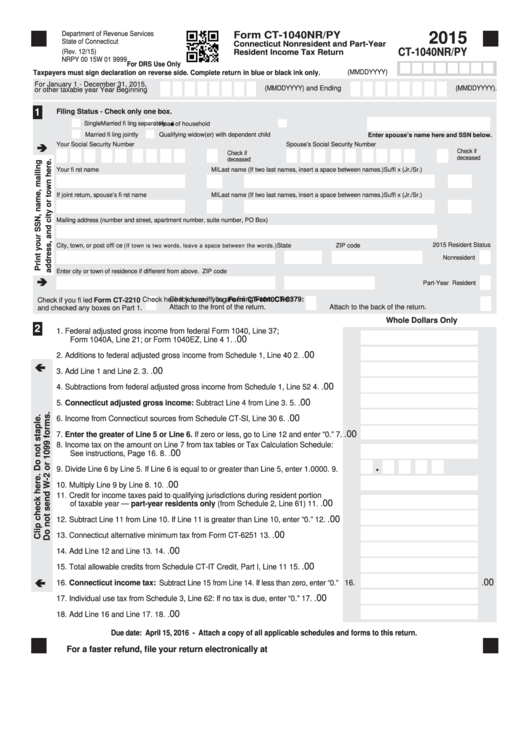
While this form is more complicated than Form 1040EZ, it allows you to itemize deductions as well as claim numerous expenses and tax credits. Even if you had no taxable income but are eligible for a tax refund or credit, this might be the correct form for you. You might have to use this form depending on your age, filing status and gross income. Other requirements apply if you want to use this simplified form. You need to meet all the requirements, such as being under 65 years old, single or married filing jointly, claiming no dependents, and with taxable income less than $100,000.

If your tax situation isn’t complicated, you might be able to take the “easy” route and file Form 1040-EZ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
